EMC compliance testing is used to confirm that an electrical or electronic device does not emit objectionable electromagnetic disturbances or does not excessive become susceptible to causes of electromagnetic disturbances in its natural habitat. The principle of its working is based on coexistence. Various equipment should be able to share the electrical infrastructure and spectrum without interfering with each other. To ensure that this is done regulators establish limits procedures and standards of acceptance which are used uniformly within the industries. Practical EMI EMC testing is done to assess two complimentary dimensions. In emissions testing, a product is examined in terms of the amount of cables and radiation that it emits into the environment. Immunity testing is involved in the determination of the behavior of the product to external electromagnetic stress.
Pass or fail does not limit it. Compliance testing provides a level of assurance that in the real-life electromagnetic conditions, the performance will be consistent. It promotes access safety of the market and quality product. The knowledge of the principle of operation explains the reason test setup is a stringent task why documentation is important and why the slightest change of settings can shift the results by several decibels.
The EMC compliance testing presents a very straightforward question on the emissions side. The amount of unwanted electromagnetic energy produced by the product and the amount that it exits the product. There are two primary paths. Waveguiding through the power and signal cables are conducted emissions. Radiated emissions are abandoned as electromagnetic fields on the product.
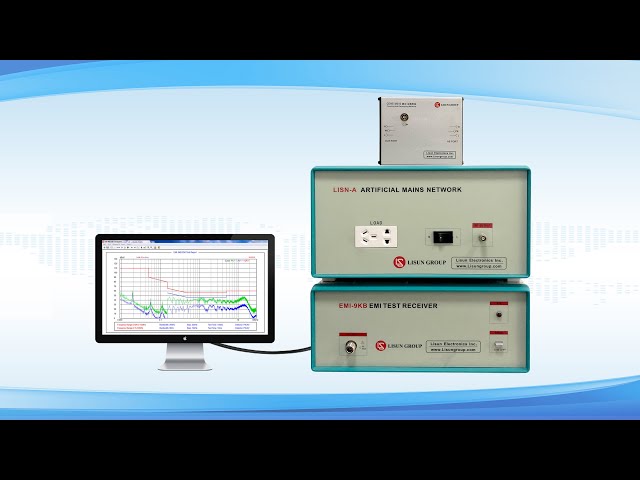
In the case of conducted emissions impedance control and measurement is the operating principle. An impedance network is added in between the product and the source of power, whereby distubances encounter a repeatable load. The disturbance voltage over this network is connected to a measuring receiver that time-scans the given frequency range over predefined bandwidths and predefined detectors. It is not just instantaneous peaks that are read by the receiver. It implements detector algorithms which simulate the effect of interference on actual radio services. Associated with fixed impedance grounding and cable geometry is repeatability.
Radiated emissions are based on far field measurement. The item is put under controlled environment and respective field strength value is measured at known distance in terms of calibrated antennas. This is the principle of spatial sampling. The test measures the highest field that may disrupt radio services by rotating the product and alternating the polarity of the antenna in order to detect the maximum values of the same. Factor of distance antenna and location attenuation are strongly held since the field strength changes at a high rate by geometry.
In either of the two directions the measurement chain consists of receivers antennas cables preamplifiers and reference planes. Calibration is necessary so as to ascertain that what is being measured is to absolute limits. The principle of operation relies on the management of all the variables that are capable of interfering with the coupling between the product and the measurement system.
In EMI EMC testing, the perspective is inverted in the immunity testing. Rather than posing how the emission of the product is, it poses how the product reacts to the electromagnetic stress when it is exerted. The principle of working is regulated exposure. Standardized fields or discharges of waveforms are used in a repeatable manner as the product is measured in terms of degradation loss of functioning or unsafe behaviour.
Conducted immunity is a disturbance which involves cables in coupling networks that do not disrupt normal functioning without imposing stress over the conduit. Radiated immunity exposes the product to an equal electromagnetic fields in a small range of frequencies. The electrostatic discharge testing involves the application of controlled discharge to those points that may be touched by the user. Surge and transient test causes high energy events that are equivalent of lightning or switching.
In all the immunity tests there is the principle of equivalence. The stress introduced should be reflective to the actual conditions and should be introduced in a manner that other laboratories would be capable of replicating it. Pass criteria are characterized by monitoring. These temporary losses that can be self-recovered may be welcome, whereas the loss of functionality or unsafe functioning is not. The test is thus a composition of physic of exposure and functional evaluation.
Environmental control is one of the vital aspects of the working principle. Testing of EMC compliance is sensitive to routing grounding cables and noise around. The reference ground plane offers a stable path of returning. The lengths and locations of cables are specified since they influence coupling. The ambient signals should be of a lesser margin in order to avoid covering the product emissions.
Laying a repeat plan is realized by documented plans and verification procedures. The environment is verified by background scans. Measurement chain is checked by reference signals. Deviations would invoke corrective action even prior to the actual testing. The field should make sure that the product is represented by the results and not the test arrangement.
Contemporary laboratories also have interaction control between various tests. Cables or grounding can be changed when high energy immunity tests are involved. The processes are to be verified prior to reversion to measurements of emissions. This sequencing does not affect the ability to measure the measurement chain.
There is conformance evidence in the form of documentation which traces outcomes down to method and conformity standards. Test plans characterize worst case settings and acceptance. Reporting involves environmental conditions of uncertainty in calibration of equipment and functional observation. This reporting enables agencies and clients to believe in findings.
System integration facilitates efficiency and precision. Decoupling networks antennas and software have been developed together. Some suppliers like LISUN give out built-in EMC where both hardware and software compliance limits variability or makes audits easier. Knowledge is not displaced because of integration. It supports the working principle, reducing the uncontrollable interfaces.
The principle of functioning of EMC compliance testing is controlled equivalence. Defined geometries and impedances are used to measure the emissions. The application of immunity is done using standardized stresses which are real world applications. The source of repeatability consists of calibration of environmental control and controlled procedures. When these factors are done well EMI EMC testing can offer sure evidence that products can be safely and reliably coexisted in the electromagnetic environment.
Tags:EMI-9KBYour email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *