Product No: SMT-TD15
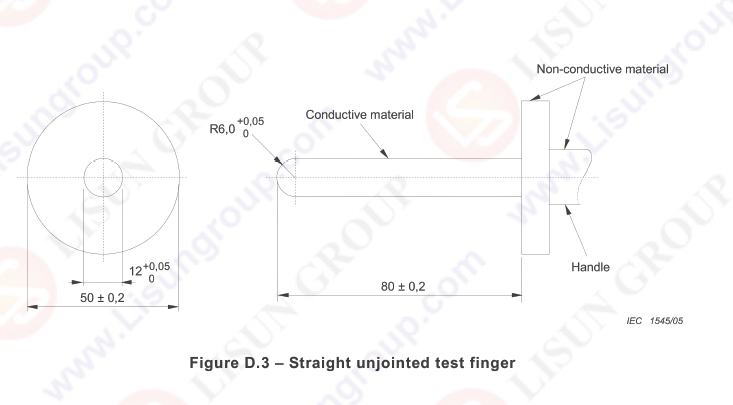
IEC 62109-1 Figure D.3 Straight Unjointed Test Finger is a specialized safety tool tailored for photovoltaic (PV) inverters and power conversion equipment. It features a rigid stainless steel “finger” that mimics human finger access—critical for verifying if hazardous live parts or high-voltage components remain inaccessible. Paired with an insulating nylon handle for safe, non-slip operation, it applies a precise 10N thrust to match real-world accidental contact. Strictly aligned with IEC 62109-1 standards, it’s durable, dimensionally stable, and essential for manufacturers/labs to ensure PV equipment safety, eliminating electric shock risks for installers and users.
Specifications:
• Probe Type: Straight Unjointed Test Finger (IEC 62109-1 Figure D.3 compliant for PV equipment)
• Finger Material: Stainless steel (rigid, corrosion-resistant, maintains dimensional accuracy under test conditions)
• Handle Material: Nylon (insulating, heat-resistant, non-slip for secure grip during high-voltage equipment testing)
Key Dimensions:
– Finger Diameter: 12 mm ± 0.1 mm
– Effective Finger Length: 80 mm ± 0.2 mm
– Total Length (Finger + Handle): 180 mm ± 0.5 mm
– Finger Tip: Hemispherical, radius 6 mm ± 0.05 mm (smooth to avoid enclosure damage)
• Applied Thrust: 10N ± 0.5N (precise force to simulate accidental human contact with PV equipment)
• Core Function: Verifies inaccessibility of hazardous live/high-voltage parts in PV inverters and power converters per IEC/UL 62109-1
Test Procedures:
• Inspect the test finger for damage (e.g., bent steel, cracked handle) to ensure testing accuracy.
• Power on the PV inverter/power converter and let it reach normal operating mode.
• Hold the nylon handle and align the straight finger with equipment openings (e.g., vent grilles, terminal covers).
• Apply steady 10N thrust to the finger toward internal hazardous parts.
• Check if the finger touches any live/high-voltage components.
• Record whether the equipment meets safety requirements (pass/fail).
Applications:
• Safety testing of grid-tied PV inverters (per IEC 62109-1Figure D.3) to block access to high-voltage parts.
• Compliance checks for off-grid PV power converters (e.g., solar charge controllers).
• Verification of residential PV micro-inverters (e.g., module-level inverters) for electric shock protection.
• Quality control for commercial PV string inverters during manufacturing for global solar markets.
• Post-production safety audits of PV energy storage converters.
Straight Unjointed Test Finger of IEC 62109-1 Figure D.3