Product No: SMT-8902
The GR-1089 Core Standard Jointed Test Finger is a specialized safety tool engineered for telecommunication and data center equipment—such as network cabinets, base stations, fiber optic transmitters, and server racks. Its 3-joint flexible design mimics the natural movement of a human finger, allowing it to navigate complex internal paths (e.g., around wiring harnesses or control modules) that rigid probes can’t reach. Crafted from conductive stainless steel (for detecting live parts) and paired with a heat-resistant insulated handle, it applies a controlled 10N thrust to test if hazardous components (e.g., exposed circuits, high-voltage terminals) are accessible. Strictly compliant with GR-1089’s NEBS (Network Equipment-Building System) requirements, it’s critical for manufacturers to ensure telecom equipment safety and meet global network infrastructure regulations.
Specifications:
Tool Type: GR-1089 Core Standard Jointed Test Finger (for telecommunication equipment hazardous part testing)
Probe Material: Heat Treated steel
Joint Characteristics: 3 pivot joints; max bending angle per joint: 90°; maintains structural integrity under 10N thrust
Key Dimensions:
– Test Finger Diameter: 12 mm
– Test Finger Length: 90 mm
– Jointed Length: 30 mm
Applied Thrust: 10N ± 0.5N (standard for NEBS testing; simulates light accidental finger contact with telecom equipment)
Core Function: Navigates complex telecom equipment internals via flexible joints; detects accessible hazardous live parts; ensures GR-1089 compliance
Test Procedures:
1. Inspect the test finger for damage (loose joints, bent probe segments, cracked insulation) and confirm conductivity with a test tool.
2. Power on the telecommunication equipment (e.g., network cabinet) and set it to normal operating mode.
3. Hold the insulated handle, use the 3-joint design to guide the probe into equipment gaps (e.g., control panel seams, wiring access slots).
4. Apply a steady 10N thrust to the probe—advance until resistance from components or enclosures is felt.
5. Check the connected live-part detection instrument for signals (indicating contact with hazardous parts).
6. Record results: Pass if no hazardous contact; Fail if live parts are accessible.
Applications:
1. Testing access to live circuits in network equipment cabinets (per GR-1089-CORE:2024 Figure 4.2.1) to prevent electric shock in data centers.
2. Verifying hazardous part access in 5G base station control modules (compliant with IEC 61032:2017) for field safety.
3. Safety checks for fiber optic transmitter wiring gaps (per UL 62368-1:2023) to protect telecom technicians.
4. Quality control for server rack power distribution units (PDUs) during manufacturing, ensuring GR-1089 compliance.
5. Post-production testing of telecom backup power equipment enclosures to meet global NEBS physical protection standards.
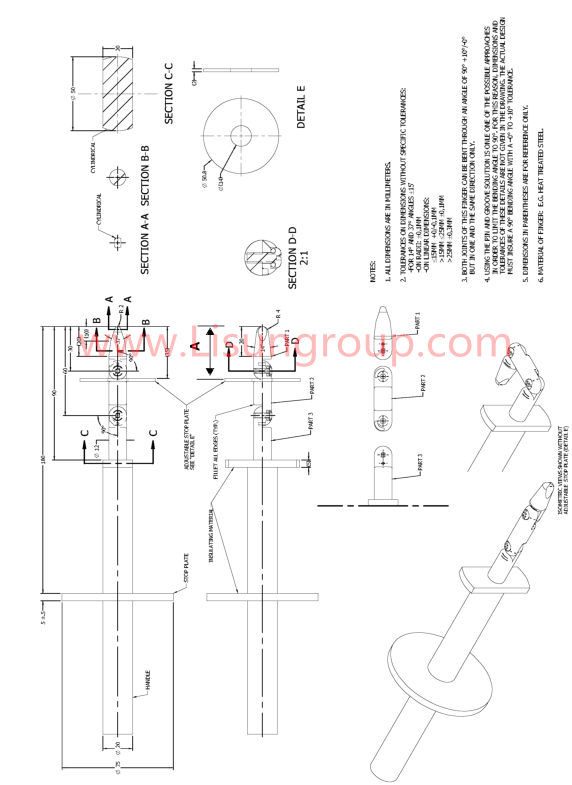
GR1089_CORE standard Jointed Test Finger